Methods of Prevention
- In the recent past, constructing defences has been the main way of dealing with the risks of flooding and coastal erosion. Physical defences remain a vitally important part of our approach to managing flood and coastal erosion risk, however they are costly to build and maintain and may not always be the most sustainable option. They can also impact on the environment, on recreation and on the appearance of an area. With climate change set to increase the risks, alternatives to physical defences are becoming more and more important. Defra has therefore been developing approaches to flood and coastal erosion risk management based around the idea of adaptation, as well as more traditional approaches to managing risk such as physical defences.
- Working with natural processes to reduce the risks
- Planning communities to reduce the risks
- Helping communities live with flooding and coastal erosion risk
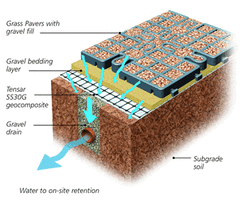
- What are Sustainable Drainage Systems (SUDS)? Sustainable Drainage Systems (SUDS) provide a more sustainable approach to draining surface water and are needed to better manage the future likelihood of flooding and water quality issues caused by these pressures. SUDS do this through mimicking natural drainage and managing water above-ground with the characteristics of storage and slowing down flows of water into sewers and water courses as well as improving water quality and amenity
- More recently, water demand has started to exceed supply, and localised flooding has become an issue. Industry experts are now recognising the important role that rainwater harvesting (also known as rainwater recycling, and grey-water recycling) has to play in alleviating both these problems.
Raised Ground Floor definition:
A flooring system having removable panels supported on adjustable pedestals or stringers to allow convenient access to the space below. Also known as access flooring; elevated flooring; pedestal flooring.
Flood Damage Prevention:
- Install a sewer backflow valve to prevent sewage from backing up into the house.
- Elevate water heaters, furnaces, washers and dryers at least six inches above basement floors or move them to an upper floor. Use a licensed contractor when making plumbing or electrical changes.
- Raise electrical panel boxes, switches, and outlets at least one foot above the 100-year flood level. For help in determining the 100-year flood level in your area, check with local officials.
- Cut drywall to at least one-half inch above the floor, especially in basements. Concrete floors commonly absorb ground moisture which travels up the wallboard allowing mould to grow unseen within the walls. Seal the gap between the wallboard and the floor with wood or rubberized floor trim.